Tips
Git / Github
__init__.py Usage
https://mmjourney.tistory.com/14
pip install, git+, pacakage
Terms explanation:
Package - A folder/directory that contains init.py file.
Module - A valid python file with .py extension.
Distribution - How one package relates to other packages and modules.
[Python] github 저장소를 pip install 설치가 가능하도록 만드는 방법
from & import
link
Why and how to use __init__.py
link from <module(file) path> import <function or class>
Undo
git reset HEAD~1
git reset --hard HEAD~1
git reset <specific commit hash>
git reset --hard <specific commit hash>
Without --hard, only undo commits, i.e, leave updates in the files.
With --hard, delete the updates as well.
HEAD is a pointer.
Two ways of merging. Not two ways. Way 1 is when I want to merge my branch to main branch, and Way 2 is when I want to merge main branch to my branch to update any changes made in main branch.
-
You can manually merge on Github UI. Run
git pushfrom a branch that you want to merge to amainbranch. Then work on conflict,merge,etc on Github UI. Note thatgit pushis not pull request. You just push your new branch to remote git repo (Github). You have to manually clickCompare & pull requeston Github.
This process is happening on remote repo. To make the update effective on local repo, you should do something likegit pull. -
Use
git mergeYou need to take care of conflict stuff on Vscode. After merging, you should do something likegit pushin amainbranch, for example, if you merged another branch tomainto make remote repo effective on the updates made in local repo.
git switch feature-branch에서 git merge main 을 하는건 main의 updates를 내 feature-branch에 반영하기 위해서임.
git switch main에서 git merge feature-branch하는건 내 feature-branch를 main에다가, i.e. main <- feature-branch merge 하기 위함. 하지만 main 이 default branch인 경우, feature-branch와 main 사이에 confict이 있다면, 즉, feature-branch를 작업하는 동안 누군가 main에 updates을 했다면, feature-branch에서 conflict되는 부분을 해결한후에야 (예를 들어 main updates내용과 기존 feature-branch 내용 모두 살린 후) merge할 수 있다. 그래서 feature-branch를 git push 한 후 Github에서 pull request 할 때 conflict가 있으면 수정해야되는데 그때 예를 들어 두 branch 내용 모두 살리는 식으로 수정하면 모든 내용이 feature-branch에 덮어씌워지게 된다. 그래야 conflict가 해결돼서 main으로 merge할 수 있으니까.
그래서 정리하자면, feature-branch에서 작업시작할 땐 항상 git merge 써서 main에서 update된 내용을 가져올 것 (다만 git pull을 써야되는 경우도 있다. 언제? 동일한 branch에서 작업할 때). main -> feature-branch.
작업이후에 main으로 merge 신청을 할 땐 git push 한후 Github UI에서 pull request 신청. 이 때 conflict 안나게 미리 앞 단계 (git merge)가 필요한 것.
Difference between git commit -am and git commit -m
link
To use git commit -am <file>, file should have already been added. I.e., this command works for the files that are modified, not newly created.
To use git commit -am, you should do git add <file> beforehand to make the file staged. Otherwise, git doesn’t know whether the file exists or not.
git commit -am 에서 a는 file의 change를 stage하기 위해서 add 하는거고 (file에 change가 있으면 이 때도 결국 gid add <file>한 후에 git commit -m 해야됨) ,
git branch output issue
git config --global pager.branch false
jupyter notebook, permission denied, docker
Clone a repo from someone else’s Github and push it to a repo on my Github
-
git remote add origin <remote repo address>: origin이란 이름의<remote repo address>나타내는 remote을 새로 만듬
error: remote origin already exists: git clone 하면 remote이름이 default로 origin이라서 이미 있는듯 -
git remote -v
origin <...> (fetch)
origin <...> (push) -
git remote rename origin upstream: 기존의 origin을 upstream으로 이름 바꿈 -
git remote add origin <repo on github>: 여기의 origin은 github에서 새로만든 repo를 나타냄<repo on github>은 내 github에서 new repo 만든거
(위 두 단계 기존의 origin을 upstream 으로 바꾸고 다시 새로운 origin을 내 new repo on my Github으로 바꾸는 거임.
이 방법 대신에
git remote set-url orign <repo on my Github> 을 써서 upstream을 만드는 대신에 origin이 가리키고 있는 remote repo 주소를 바꿈)
$ git remote # returns remote repos currently connected to current local repo
origin
upstream
-
git checkout -b origin: create a branch “origin” (branch “main”은 이미 있던듯)
따라서 현재 local repo에 branch가 “origin”, “main” 두 개
$ git branch # I believe this returns branches in local repo
main
* origin
git checkout main
$ git branch
* main
origin
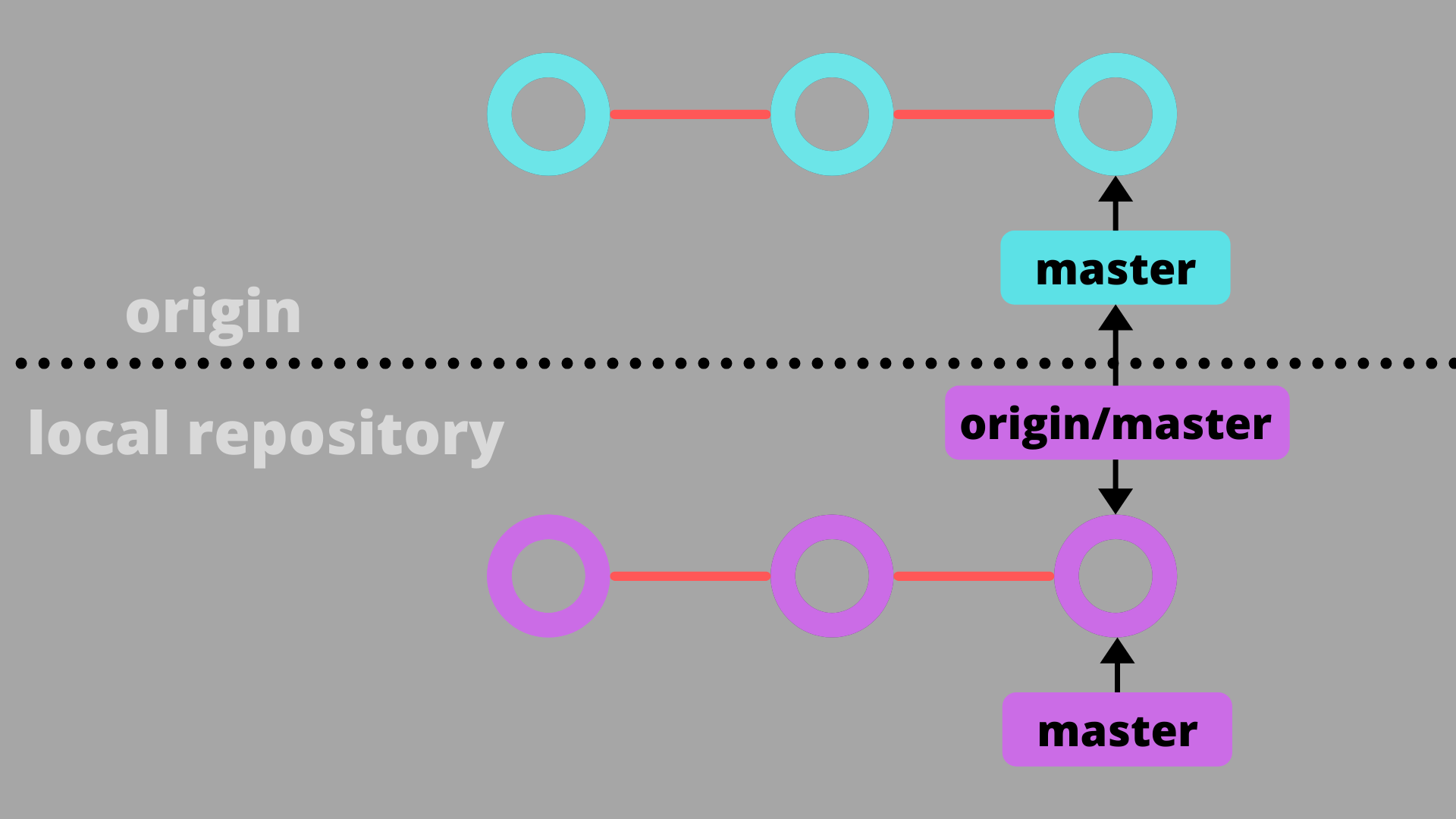
Note. Your branch is up to date with 'origin/main' : 여기서 ‘origin/main’은 remote tracking branch 인데
결국 origin denotes remote URL and master denote the remote branch it is tracking. 즉 저 메세지는 remote repo의 origin/master과 local repo의 main branch가 sync 돼있다는 말.
git checkout -b <branch_name> vs git branch <branch_name>
git checkout -b <branch_name>: creates a new branch and checks out (switch to) the new branch git branch <branch_name>: creates a new branch but leaves you on the same branch git checkout <branch_name>: check out (switches to) a new branch (copy from remote)
Note that if you were on master branch and run git branch new_branch, both master and new_branch now point to the same commit.
There are more: git switch -c new_branch, git switch, etc
Cloning a repo from someone else’s Github and pushing it to a repo on my Github
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18200248/cloning-a-repo-from-someone-elses-github-and-pushing-it-to-a-repo-on-my-github
- Create a new repository at http://github.com (don’t initialize README, .gitignore, license)
- Clone a repo of someone else’s to my local machine
git clone
There’s also a way of using fork.
Both methods can be used to update original github repo from my local repo. But fork can be used to pull request my change when I don’t have authority to update a repo
Indicate message of title and description for each commit you make
git commit -m "title" -m "Descripton
commit isn’t alive on Github unless you do git push.
local machine에서 폴더 만든 후 git push 하기
- local machine에서 폴더를 만든 후 작업을 한다.
- 해달 디렉토리에서
git init실행한다. - Github에서 새 repository를 생성한다.
- 터니멀에서
git remote add origin <ssh 주소>실행한다.<ssh 주소>는 3 에서 만든 repo의 ssh 주소. -
git remote -v실행해서 현재의 local repo 에 연결된 remote repositories 목록을 확인한다. -
git push origin master실행한다.origin master를 생략하고 싶으면git push -u origin master를 실행해서 upstream을 설정한다. 즉 default로 어디로 push 하고싶은지 설정한다.
Git Commands
git init basically means to turn a current directory into a git repository (in a local machine).
vim text editor
Modes
normal mode (first screen I see after running the editor), insert mode (by hitting i), visual mode (by hitting v)
Move cursor left right as a word
shift + left right arrow
Display line number
:set number
Move without arrow keys
In normal mode j : down
k : up
h : left
l : right
shift+left,right : move to start and end of a line
Delete
In normal mode, use x (delete a character) or dd (delete a line)
To delete a block, v + select a block + d
Undo / Redo
In normal mode, hit u for undo.
ctrl + r for redo.
Show line numbers
:set number
Move to a line
:2 : go to line number 2
Copy and Paste
Go to visual mode by hitting v.
Press y to copy, d to cut.
Press p to paste
Notice. If vim --version says -clipboard, run sudo apt-get install vim-gtk3 -y to use mouse drag, cmd+c, cmd+v for copy and paste.
Use a mouse to locate a cursor
link
Run sudo vi /etc/vim/vimrc and uncomment set mouse=a (delete " at the front). We need sudo because vimrc is a read-only file.
Docker
About user and group in a container
If run a container without adding user,
echo $UID in a container shell returns 0. (It’s 1001 in host PC)
link
In the context of a Dockerfile, you can use a USER directive as often as you need to switch users.
FROM some-base-image-with-a-non-root-user
USER root
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install ...
USER nonroot
Add a user and group
ARG USERNAME=user-name-goes-here
ARG USER_UID=1000
ARG USER_GID=$USER_UID
# Create the user
RUN groupadd --gid $USER_GID $USERNAME \
&& useradd --uid $USER_UID --gid $USER_GID -m $USERNAME \
#
# [Optional] Add sudo support. Omit if you don't need to install software after connecting.
&& apt-get update \
&& apt-get install -y sudo \
&& echo $USERNAME ALL=\(root\) NOPASSWD:ALL > /etc/sudoers.d/$USERNAME \
&& chmod 0440 /etc/sudoers.d/$USERNAME
# ********************************************************
# * Anything else you want to do like clean up goes here *
# ********************************************************
# [Optional] Set the default user. Omit if you want to keep the default as root.
USER $USERNAME
ARG UID=
ARG USER_NAME=
# Recommended to use useradd not adduser
RUN adduser $USER_NAME -u $UID --quiet --gecos "" --disabled-password && \
echo "$USER_NAME ALL=(root) NOPASSWD:ALL" > /etc/sudoers.d/$USER_NAME && \
chmod 0440 /etc/sudoers.d/$USER_NAME
Why run a docker container as a non-root user
Running a Docker container as a non-root user
Docker Container를 root가 아닌 일반 유저로 실행시키는 법
Understanding how uid and gid work in Docker containers
Just a note
#ENV PATH /usr/local/envs/$CONDA_ENV_NAME/bin:$PATH
base /usr/local
dfm /usr/local/envs/dfm
vs
/usr/local
base /usr/local/envs/dfm
Pytorch docker file
nvidia-docker is deprecated
To check whether nvidia containter toolkit is installed, use nvidia-ctk --version
CUDA Programming
cuda설치해서 pytorch를 쓰는데 이 말은 pytorch써서 코드를 쓰면 그걸 gpu를 사용하게 해주는 cuda programming이 있다는 얘기. 즉 cuda programming 한다는말은 내가 쓴 코드가 gpu를 쓰게끔 한다는 말.
link This link well explains about the relations between CUDA,PyCUDA, C++, etc.
“CUDA programming model allows software engineers to use a CUDA-enabled GPUs for general purpose processing in C/C++ and Fortran, with third party wrappers also available for Python, Java, R, and several other programming languages.”
Here, thire party wrappers include PyCUDA. I.e., C++는 third party 없이 바로 가능하고, Python의 경우 PyCUDA를 써야된다?
“Compute Unified Device Architecture (CUDA) is a parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) created by Nvidia in 2006, that gives direct access to the GPU’s virtual instruction set for the execution of compute kernels.”
API는 functions 등이 갖춰져있는 interface이고 kernel은 함수 정도로 이해.
Pytorch
pretty print
from pprint import pprint
pprint
generator
model_1.parameters()
list(model_1.parameters())
for p in model_1.parameters():
print(p)
def nextSquare():
i = 1
# An Infinite loop to generate squares
while True:
yield i*i
i += 1
if i > 10:
break
for num in nextSquare():
print(num)
CCV (Oscar)
Complaining about CUDA
Dont forget to load cuda module load cuda/x.x
Choose a specific gpu
link Use the names of gpu at the bottom of the page
For ex,
interact -q gpu -f geforce3090 -g 1 -m 40g -n 4 -t 1:00:00
VScode
diable auto activate virtual environment on vscode
link
Check out the second answer.
cmd + shift + p -> json ssh setting (because I want to change vscode setting of sshed machine)
-> type the following
{
"terminal.integrated.defaultProfile.linux": "bash", # this is for default terminal
"python.terminal.activateEnvironment": false,
}
Linux
nvidia cuda toolkit multiple versions
Shouldn’t just install deb files. Also, follow specfic instructions installing .run local files.
link
This also covers this topic.
link
Installing nvidia driver
(This process is called “Install NVIDIA Drivers with Ubuntu Repository using CLI”)
sudo apt autoremove nvidia* --purge
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade <- I don’t know if this helped but I did it
ubuntu-drivers devices <- I first installed 545 but had an issue. So did
sudo apt autoremove nvidia* --purge sudo apt install nvidia-driver-545
sudo reboot
There’s also a method “Install NVIDIA Drivers using graphics-drivers/ppa on Ubuntu”
Stick to using Ubuntu Repository if possible
apt, apt-get, aptitude
Sometimes aptitude helps a lot.
Be cautious when updating nvidia driver and installing nvidia cuda toolkit
SSH
brown related ssh
There is a way to access Brown CS’s file system on CCV
ssh brown works because I have the following in Mac’s ~/.ssh/config
ssh jha38@ssh.cs.brown.edu also works.
Host brown
HostName ssh.cs.brown.edu
ForwardX11Trusted yes
User jha38
/data/jhtlab locates at Brown CS’s file system. After sshing into brown, do cd ../../data/jhtlab/jha38
to find my folder.
James said there’s a way to access Brown CS’s file system (/data/jhtlab/jha38) on CCV (ssh oscar)
ssh key pair
link
I had an issue with sshing to hotcake / cake after regenerating ssh key pair.
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub jun@hotcake this helped.
This copy public ssh key to server’s authorized_keys folder which is located under server’s ~/.ssh.
After that, I can ssh into server just by ssh hotcake or ssh cake. For this, I guess I need to edit configure file config under Mac’s ~/.ssh.
For example,
Host cake
HostName cake
User junsukha
MLops
basic usage of psycopg
Basic module usage — Psycopg 2.9.9 documentation
close and remove a container
docker stop "CONTAINTER ID"
docker rm "CONTAINER ID"
Use docker ps -a to see all containers
host, container
docker run -p 127.0.0.1:80:8080/tcp
This means to bind port 8080 of the container to TCP port 80 on 127.0.0.1 of the host machine.
Any installation in a running container will be lost as soon as exiting the container
dockerfile - Install package in running docker container - Stack Overflow
add port tunneling between mac (local) and linux (remote) insidee a linux (remote), i.e. I ssh into linux (remote) from mac (local)
press shift and ~ and c. Hold shift while hitting ~ and c.
-L 8888:hotcake:8888 : connect mac’s 8888 to hotcake’s (server) 8888.
openssh - Add port forwarding to a running SSH session - Unix & Linux Stack Exchange
multiple port tunneling when ssh
ssh -L forward multiple ports - Stack Overflow
how to find a docker host machine’s ip address from inside a container?
sudo ip addr show docker0 gives ip address of docker host machine (in my case 172.17.0.1)
Also can identify ip address by docker network inspect bridge
Both commands above are run in hotcake (the machine sshed into)
To see an ip address of a container, run ip addr show eth0 inside a container.
- ex:
root@e77f6a1b3740:/# ip addr show eth0
03. Model Registry 2) Save Model to Registry
os.environ["MLFLOW_S3_ENDPOINT_URL"] = "http://172.17.0.1:9005" # when running in a container, should use host ip address instead of localhost?
os.environ["MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI"] = "http://172.17.0.1:5001"
Orignal version uses "http://localhost:9005" and "http://localhost:5001". 9005 and 5001 are ports of Linux (remote machine) and are connected to 9091 and 9092 of mac (local) individually.
How to debug inside a container with vscode
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w77D5KuJ7eE
I think there are two ways: 1) access to a container with vscode from local (mac) 2) access to a conatiner with vscode from remote (linux); need to ssh from mac first
Method 1): follow the video
Method 2):
- Install
Remote Developmentextension (I thought, for this method, the extension should be installed in linux machine but accessing container also works when the extension is installed on mac) - click a bottom left button and select
access to running container - choose a container (only currently running containers are visible)
DL
c++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class GfG {
public:
static int x;
GfG() {
x++;
}
// static member function
// static void printMsg() { cout << "Welcome to GfG!" << x; }
};
int GfG::x = 3; // just like static member function
// main function
int main()
{
GfG obj1;
cout << obj1.x << endl;
obj1.x++;
GfG obj2;
cout << obj2.x << endl;
// invoking a static member function
// GfG::printMsg();
}
Pytorch
torch includes cuda toolkit
pytorch binary includes cuda toolkit. But it’s not a bad idea to match local cuda toolkit and torch cuda toolkit.
keywords: pytorch binary, build from source
CUDA related issue while running a model
First thing to try is different versions; different python, pytorch, cuda versions.
torch 2.0.x has issue with cuda
Don’t use torch 2.0.x versions.
ETC
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: